Share
A 9.02-g sample of liquid water at 40.3 °C is heated by the addition of 203.93 J of energy. The final temperature of the water is ________ °
Question
A 9.02-g sample of liquid water at 40.3 °C is heated by the addition of 203.93 J of energy. The final temperature of the water is ________ °C. The specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.184 J/gK.
in progress
0
Chemistry
3 years
2021-08-30T01:19:51+00:00
2021-08-30T01:19:51+00:00 1 Answers
3 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
45.70 C
Explanation:
We’ll use the formula for specific heat Q=mcΔT. Let’s first check out units and look at the values we have.
Q=heat= 203.93 J
m=mass= 9.02g
c= specific heat= 4.184 J/g K
ΔT= Change in temperature= Final temp. – initial temp. =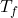 –
– 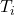
Let’s plug in what we know.
203.93 J = (9.02g)(4.184)(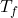 – 40.3 C)
– 40.3 C)
We’ll just solve this algebraically to solve for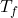 . It’s like solving for x, just a different variable. It’s easier to do the more complicated side first and then start moving your numbers to the other side.
. It’s like solving for x, just a different variable. It’s easier to do the more complicated side first and then start moving your numbers to the other side.
203.93 = (37.73)(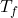 – 40.3) We’ll multiply 37.73 by
– 40.3) We’ll multiply 37.73 by 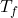 AND 40.3 so we’ll get…
AND 40.3 so we’ll get…
203.93 = (37.73Tf – 1520.5)
Let’s start moving numbers to the other side
203.93 + 1520.5 = 37.73Tf
1724.4 = 37.73Tf
45.70 C=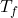
This makes sense with our problem since they heated water, so we should see an increase in temperature.