Share
The driver of a 770 kg car decides to double the speed from 23.1 m/s to 46.2 m/s. What effect would this have on the amount of work required
Question
The driver of a 770 kg car decides to double the speed from 23.1 m/s to 46.2 m/s. What effect would this have on the amount of work required to stop the car, that is, on the kinetic energy of the car? Give your answers to the following questions in joules.
in progress
0
Physics
3 years
2021-08-11T20:00:05+00:00
2021-08-11T20:00:05+00:00 1 Answers
58 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
The final kinetic energy is four times of initial kinetic energy when speed of the car doubles.
Explanation:
Mass of the car = 770 kg
initial speed = 23.1
= 23.1 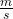
Final speed = 46.2
= 46.2 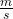
Initial kinetic energy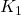 =
= 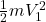
⇒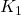 = 0.5 × 770 ×
= 0.5 × 770 × 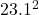
⇒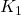 = 205440 J
= 205440 J
Final kinetic energy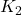 =
= 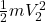
⇒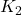 = 0.5× 770 ×
= 0.5× 770 × 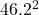
⇒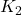 = 821760 J
= 821760 J
Thus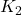 = 4
= 4 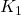
Therefore the final kinetic energy is four times of initial kinetic energy when speed of the car doubles.