Share
Two identical wheels, wheel 1 and wheel 2, initially at rest begin to rotate with constant angular accelerations α. After rotating through t
Question
Two identical wheels, wheel 1 and wheel 2, initially at rest begin to rotate with constant angular accelerations α. After rotating through the same angular displacement, Δθ0, the angular velocity of wheel 1 is ω1 and the angular velocity of wheel 2 is ω2=3ω1. How does the angular acceleration of wheel 2, α2, compare to the angular acceleration of wheel 1, α1?a. a2 = a1b. a2 = a1/3c. a2 = 3a1d. a2 = 9a1
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-07-14T09:05:58+00:00
2021-07-14T09:05:58+00:00 1 Answers
34 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
d. a2 = 9a1
Explanation:
We can apply the following equation of motion to calculate the angular acceleration:
Since both wheel starts from rest, their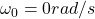
We can take the equation for the 1st wheel, divided by the equation by the 2nd wheel:
As they were rotating through the same angular displacement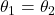 , these 2 cancel out
, these 2 cancel out
So d is the correct answer