Share
The inner and outer surfaces of a cell membrane carry a negative and positive charge, respectively. Because of these charges, a potential di
Question
The inner and outer surfaces of a cell membrane carry a negative and positive charge, respectively. Because of these charges, a potential difference of about 0.078 V exists across the membrane. The thickness of the membrane is 7.1 x 10-9 m. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the membrane?
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-22T04:40:46+00:00
2021-08-22T04:40:46+00:00 1 Answers
12 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
Explanation:
Given:
Potential difference across the membrane (ΔV) = 0.078 V
Thickness of the membrane (Δx) = 7.1 × 10⁻⁹ m
Magnitude of electric field (|E|) = ?
We know that, the electric field due to a potential difference (ΔV) across a distance of Δx is given as:
So, the magnitude of the electric field is calculated by ignoring the negative sign and thus is given as:
Plug in the given values and solve for ‘|E|’. This gives,
Therefore, the magnitude of the electric field in the membrane is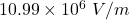 .
.