Share
The fracture strength of a certain type of manufactured glass is normally distributed with a mean of 509 MPa with a standard deviation of 17
Question
The fracture strength of a certain type of manufactured glass is normally distributed with a mean of 509 MPa with a standard deviation of 17 MPa. (a) What is the probability that a randomly chosen sample of glass will break at less than 509 MPa
in progress
0
Mathematics
4 years
2021-08-05T08:43:09+00:00
2021-08-05T08:43:09+00:00 1 Answers
20 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
0.5 = 50% probability that a randomly chosen sample of glass will break at less than 509 MPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Normal Probability Distribution
Problems of normal distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean and standard deviation
and standard deviation  , the z-score of a measure X is given by:
, the z-score of a measure X is given by:
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the p-value, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
Mean of 509 MPa with a standard deviation of 17 MPa.
This means that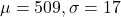
What is the probability that a randomly chosen sample of glass will break at less than 509 MPa?
This is the p-value of Z when X = 509. So
0.5 = 50% probability that a randomly chosen sample of glass will break at less than 509 MPa