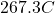Share
Argon gas enters steadily an adiabatic turbine at 900 kPa and 450C with a velocity of 80 m/s and leaves at 150 kPa with a velocity of 150 m
Question
Argon gas enters steadily an adiabatic turbine at 900 kPa and 450C with a velocity of 80 m/s and leaves at 150 kPa with a velocity of 150 m/s. The inlet area of the turbine is 60 cm2. If the power output of the turbine is 250 kW, determine the exit temperature of the argon.
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-05T20:04:53+00:00
2021-08-05T20:04:53+00:00 1 Answers
589 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
Temperature at the exit =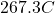
Explanation:
For the steady energy flow through a control volume, the power output is given as
Inlet area of the turbine =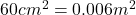
To find the mass flow rate, we can apply the ideal gas laws to estimate the specific volume, from there we can get the mass flow rate.
Assuming Argon behaves as an Ideal gas, we have the specific volume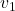
as
for Ideal gasses, the enthalpy change can be calculated using the formula
hence we have
Note: to convert the Kinetic energy term to kilojoules, it was multiplied by 1000
evaluating the above equation, we have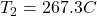
Hence, the temperature at the exit =