Share
An ideal gas is taken through a Carnot cycle. The isothermal expansion occurs at 290°C, and the isothermal compression takes place at 50.0°C
Question
An ideal gas is taken through a Carnot cycle. The isothermal expansion occurs at 290°C, and the isothermal compression takes place at 50.0°C. The gas takes in 1.36 103 J of energy from the hot reservoir during the isothermal expansion. Find the energy expelled to the cold reservoir in each cycle and the net work done by the gas in each cycle.
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-14T19:04:06+00:00
2021-08-14T19:04:06+00:00 1 Answers
38 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
the energy expelled to the cold reservoir in each cycle = 0.78×10³ J
the net work done by the gas in each cycle = 0.58 × 10³ J
Explanation:
Given that the isothermal expansion occurs at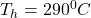
= (290+273)K
= 563 K
Isothermal compression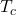 occurs at 50°C
occurs at 50°C
= (50+273)K
= 323 K
The amount of energy absorbed by the gas from the hot reservoir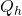
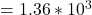 J
J
a) The amount of energy expelled to the cold reservoir in each cycle can be calculated by using the formula:
= 780.25
= 0.78×10³ J
b) the net work done by the gas in each cycle is as follows:
W = 580
W = 0.58 × 10³ J