Share
A student standing on a stationary skateboard tosses a textbook with a mass of mb = 1.95 kg to a friend standing in front of him. The studen
Question
A student standing on a stationary skateboard tosses a textbook with a mass of mb = 1.95 kg to a friend standing in front of him. The student and the skateboard have a combined mass of mc = 86 kg and the book leaves his hand at a velocity of vb = 4.54 m/s at an angle of 38° with respect to the horizontal.
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-05T21:00:02+00:00
2021-08-05T21:00:02+00:00 2 Answers
133 views
0

Answers ( )
Complete Question
A student standing on a stationary skateboard tosses a textbook with a mass of mb = 1.95 kg to a friend standing in front of him. The student and the skateboard have a combined mass of mc = 86 kg and the book leaves his hand at a velocity of vb = 4.54 m/s at an angle of 38° with respect to the horizontal.
a)Write an equation for the magnitude of the velocity of the student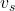 after throwing the book
after throwing the book
b) Calculate the magnitude of the velocity of the student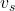 in meter per second
in meter per second
c What is the magnitude of the momentum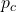 which was transferred from the skateboard to the Earth during the time the book is being thrown in kilogram meter per second
which was transferred from the skateboard to the Earth during the time the book is being thrown in kilogram meter per second
Answer:
a
The Equation is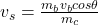
b
The magnitude of the for the velocity of the student is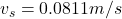
c
The momentum is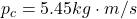
Explanation:
From the question e are told that
mass of the text book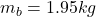
mass of student and skateboard is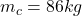
The initial velocity of the book is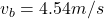
The angle made is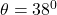
From the law of conservation of momentum along horizontal direction this can be mathematically represented as
Making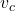 the subject
the subject
Since the total velocity of the skateboard and the student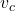 would also be the velocity of the of the student
would also be the velocity of the of the student 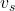
Hence
Now substituting values
The magnitude of the momentum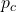 is mathematically represented as
is mathematically represented as
Here this momentum is acting vertically opposite which is indicated by the resolution for the momentum to the vertical component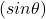
Substituting values
The question is not complete. The missing part of the question says;
a)Calculate the magnitude of the velocity of the student, v_s in meters per second.
b)What is the magnitude of the momentum, pe, which was transferred from the skateboard to the the Earth during the time the book is being thrown (in kilogram meters per second)?
Answer:
A) v_s = 0.081 m/s in an opposite direction to that of the book.
B) P_e = 5.45 Kg.m/s in downward direction.
Explanation:
We are given;
Mass of the book m_b = 1.95 kg
Mass of the student and the skateboard m_c = 86 kg
Velocity of the book v_b = 4.54 m/s
Angle of projection θ = 38°
A) Using principle of conservation of momentum;
The horizontal component of the velocity of book is given as;
V_bx = V_b cos θ
Now, the book and the student are initially at rest, and so their initial momentum is zero in both horizontal and vertical direction.
Thus,
Initial momentum = final momentum
0 = m_b•v_b•cos θ + m_c•v_s
Let’s make v_s the subject of the formula;
v_s = -[m_b•v_b•cos θ]/m_c
Plugging in the relevant values to get ;
v_s = -[1.95•4.54•cos 38]/86
v_s = -0.081 m/s
The minus sign indicates that the direction of the velocity of the student is opposite to that of the book.
B) The vertical component of the velocity of book is given as;
V_by = V_b sin θ
In this vertical direction, the student is not moving, because he transfers his momentum. The momentum transferred to the earth is equal to the vertical component of the book’s momentum in magnitude but opposite in direction. Thus;
P_e = -P_ey
P_e = – m_b•v_b•sinθ
Thus, plugging in the relevant values to get ;
P_e = -1.95 x 4.54 sin38
P_e = -5.45 Kg.m/s
The minus sign indicates that the direction of momentum is downwards