Share
A point charge q1 is at the center of a sphere of radius 20 cm. Another point charge q2 = 5 nC is located at a distance r = 30 cm from the c
Question
A point charge q1 is at the center of a sphere of radius 20 cm. Another point charge q2 = 5 nC is located at a distance r = 30 cm from the center of the sphere. If the net flux through the surface of the sphere is 800 N.m2 /C, find q
in progress
0
Physics
3 years
2021-08-02T00:42:14+00:00
2021-08-02T00:42:14+00:00 1 Answers
8 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
Explanation:
Gauss’s Law says that the electric flux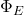 through a closed surface is directly proportional to the charge
through a closed surface is directly proportional to the charge 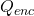 inside it. More precisely,
inside it. More precisely,
This means what is outside this closed surface does not contribute to the flux through it because field lines that go in must come out, resulting a zero flux from an external charge.
does not contribute to the flux through it because field lines that go in must come out, resulting a zero flux from an external charge.
In our context, this means the charge which is outside the sphere will have zero flux through the surface; therefore, Gauss’s law will only be concerned with charge
which is outside the sphere will have zero flux through the surface; therefore, Gauss’s law will only be concerned with charge  which is inside the sphere; Hence,
which is inside the sphere; Hence,
Solving for gives
gives
which is the charge inside the sphere.