Share
A beaker contains 0.500 kg of water at a temperature of 3.0 °C. The beaker is heated, and the internal energy of the water incr
Question
A beaker contains 0.500 kg of water at a temperature of 3.0 °C. The beaker is heated, and the
internal energy of the water increases by 21.0 kJ.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / (kg °C).
What is the temperature of the water after it has been heated?
in progress
0
Physics
3 years
2021-07-25T20:16:54+00:00
2021-07-25T20:16:54+00:00 2 Answers
488 views
1

Answers ( )
Answer:
13°C
Explanation:
We can apply the formula for Heat energy gained by a body. It is given as:
where m = mass of the body
c = Specific heat capacity of the body
For the water in the beaker, we are given that:
m = 0.5 kg
H = 21 kJ = 21000 J
c = 4200 J/kg°C
Hence, the final temperature of the water is:
of the water is:
21000 = 0.5 * 4200 * ( – 3)
– 3)
21000 = 2100 * ( – 3)
– 3)
( – 3) =
– 3) = 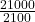
The final temperature of the water is 13°C.
Answer:
The temperature of the water after it has been heated is 13°C
Explanation:
Heat capacity H is expressed as shown :
H = mc∆t
H is the internal energy of the water
m is the mass of the water
c is the specific heat capacity of the water
∆t is the change temperature
Given H = 21kJ = 21,000Joules
m = 0.500kg
c = 4200 J / (kg °C).
∆t = t2-t1
t2 is the final temperature
t1 is the initial temperature = 3°C
Substituting the parameters;
21000 = 0.5(4200)(t2- 3)
21000 = 2100(t2-3)
21000 = 2100t2 – 6300
2100t2 = 21000+6300
2100t2 = 27300
t2= 27300/2100
t2 = 13°C