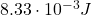Share
A 13.5 μF capacitor is connected to a power supply that keeps a constant potential difference of 22.0 V across the plates. A piece of materi
Question
A 13.5 μF capacitor is connected to a power supply that keeps a constant potential difference of 22.0 V across the plates. A piece of material having a dielectric constant of 3.55 is placed between the plates, completely filling the space between them.Part A. How much energy is stored in the capacitor before the dielectric is inserted?
Part B. How much energy is stored in the capacitor after the dielectric is inserted?
Part C. By how much did the energy change during the insertion?
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-27T10:20:44+00:00
2021-08-27T10:20:44+00:00 1 Answers
13 views
0

Answers ( )
a)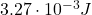
b)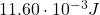
c)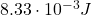
Explanation:
a)
The energy stored in a capacitor is given by
where
C is the capacitance of the capacitor
V is the potential difference across the plates of the capacitor
For the capacitor in this problem, before insering the dielectric, we have:
V = 22.0 V is the potential difference across it
Therefore, the initial energy stored in the capacitor is:
b)
After the dielectric is inserted into the plates, the capacitance of the capacitor changes according to:
where
k = 3.55 is the dielectric constant of the material
C is the initial capacitance of the capacitor
Therefore, the energy stored now in the capacitor is:
where:
V = 22.0 V is the potential difference across the plate
Substituting, we find:
C)
The initial energy stored in the capacitor, before the dielectric is inserted, is
The final energy stored in the capacitor, after the dielectric is inserted, is
Therefore, the change in energy of the capacitor during the insertion is:
So, the energy of the capacitor has increased by