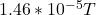Share
One long wire lies along an x axis and carries a current of 43 A in the positive x direction. A second long wire is perpendicular to the xy
Question
One long wire lies along an x axis and carries a current of 43 A in the positive x direction. A second long wire is perpendicular to the xy plane, passes through the point (0, 5.1 m, 0), and carries a current of 72 A in the positive z direction. What is the magnitude of the resulting magnetic field at the point (0, 0.60 m, 0)
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-09T12:28:54+00:00
2021-08-09T12:28:54+00:00 1 Answers
10 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
Explanation:
Using the magnetic field equation:
where:
I = current in the wire
r = distance from the wire to the point
Magnetic field due to the wire on the x- axis can be calculated as:
Magnetic field due to the positive z-direction wire:
Now; adding these two vector components together to get the magnitude of the resultant vector; we have:
=
=