Share
7. A double-slit experiment uses coherent light of wavelength 633 nm with a slit separation of 0.100 mm and a screen placed 2.0 m away. (a)
Question
7. A double-slit experiment uses coherent light of wavelength 633 nm with a slit separation of 0.100 mm and a screen placed 2.0 m away. (a) What is the distance between first-order and second-order bright fringes?
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-07-19T05:25:20+00:00
2021-07-19T05:25:20+00:00 1 Answers
31 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
The distance between first-order and second-order bright fringes is 12.66mm.
Explanation:
The physicist Thomas Young establishes through its double slit experiment a relationship between the interference (constructive or destructive) of a wave, the separation between the slits, the distance between the two slits to the screen and the wavelength.
Where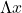 is the distance between two adjacent maxima, L is the distance of the screen from the slits,
is the distance between two adjacent maxima, L is the distance of the screen from the slits,  is the wavelength and d is the separation between the slits.
is the wavelength and d is the separation between the slits.
The values for this particular case are:
Notice that is necessary to express L and in units of milimeters.
in units of milimeters.
Finally, equation 1 can be used:
Hence, the distance between first-order and second-order bright fringes is 12.66mm.