Share
Block 1, of mass m1 = 2.50 kg , moves along a frictionless air track with speed v1 = 27.0 m/s. It collides with block 2, of mass m2 = 33.0 k
Question
Block 1, of mass m1 = 2.50 kg , moves along a frictionless air track with speed v1 = 27.0 m/s. It collides with block 2, of mass m2 = 33.0 kg , which was initially at rest. The blocks stick together after the collision.A. Find the magnitude pi of the total initial momentum of the two-block system. Express your answer numerically.B. Find vf, the magnitude of the final velocity of the two-block system. Express your answer numerically.C. what is the change deltaK= Kfinal- K initial in the two block systems kinetic energy due to the collision ? Express your answer numerically in joules.
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-09-01T12:08:18+00:00
2021-09-01T12:08:18+00:00 1 Answers
7 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
a
The total initial momentum of the two-block system is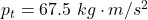
b
The magnitude of the final velocity of the two-block system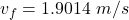
c
the change ΔK=Kfinal−Kinitial in the two-block system’s kinetic energy due to the collision is
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of first block is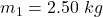
The initial velocity of first block is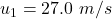
The mass of second block is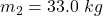
initial velocity of second block is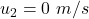
The magnitude of the of the total initial momentum of the two-block system is mathematically repented as
substituting values
According to the law of linear momentum conservation
Where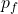 is the total final momentum of the system which is mathematically represented as
is the total final momentum of the system which is mathematically represented as
Where is the final velocity of the system
is the final velocity of the system
substituting values
The change in kinetic energy is mathematically represented as
Where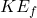 is the final kinetic energy of the two-body system which is mathematically represented as
is the final kinetic energy of the two-body system which is mathematically represented as
substituting values
While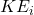 is the initial kinetic energy of the two-body system
is the initial kinetic energy of the two-body system
substituting values
So