Share
A 2 kg rubber ball is thrown at a wall horizontally at 3 m/s, and bounces back the way it came at an equal speed. A 2 kg clay ball is also t
Question
A 2 kg rubber ball is thrown at a wall horizontally at 3 m/s, and bounces back the way it came at an equal speed. A 2 kg clay ball is also thrown at the same speed horizontally at the wall, but sticks to it upon hitting. [THE CLAY BALL / THE RUBBER BALL /NEITHER] (circle one) exerts a greater magnitude of impulse on the wall. Briefly explain (either in words or calculations)
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-08-22T04:04:46+00:00
2021-08-22T04:04:46+00:00 1 Answers
14 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
THE RUBBER BALL
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of the rubber ball is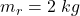
The initial speed of the rubber ball is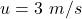
The final speed at which it bounces bank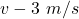
The mass of the clay ball is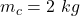
The initial speed of the clay ball is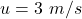
The final speed of the clay ball is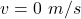
Generally Impulse is mathematically represented as
where is the change in the linear momentum so
is the change in the linear momentum so
For the rubber is
=>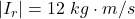
For the clay ball
=>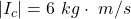
So from the above calculation the ball with the a higher magnitude of impulse is the rubber ball