Share
A physics student of mass 43.0 kg is standing at the edge of the flat roof of a building, 12.0 m above the sidewalk. An unfriendly dog is ru
Question
A physics student of mass 43.0 kg is standing at the edge of the flat roof of a building, 12.0 m above the sidewalk. An unfriendly dog is running across the roof toward her. Next to her is a large wheel mounted on a horizontal axle at its center. The wheel, used to lift objects from the ground to the roof, has a light crank attached to it and a light rope wrapped around it; the free end of the rope hangs over the edge of the roof. The student radius 0.300 m and a moment of inertia of 9.60 kg m^2 for rotation about the axle, how long does it take her to reach the side walk, and how fast will she be moving just beofre she lands?
in progress
0
Physics
4 years
2021-09-01T00:40:23+00:00
2021-09-01T00:40:23+00:00 1 Answers
122 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
The speed of the student just before she lands, v₂ is approximately 8.225 m/s
Explanation:
The given parameters are;
The mass of the physic student, m = 43.0 kg
The height at which the student is standing, h = 12.0 m
The radius of the wheel, r = 0.300 m
The moment of inertia of the wheel, I = 9.60 kg·m²
The initial potential energy of the female student, P.E.₁ = m·g·h₁
Where;
m = 43.0 kg
g = The acceleration due to gravity ≈ 9.81 m/s²
h = 12.0 h
∴ P.E.₁ = 43 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 12.0 m = 5061.96 J
The kinetic rotational energy of the wheel and kinetic energy of the student supporting herself from the rope she grabs and steps off the roof, K₁, is given as follows;
The initial kinetic energy, 1/2·m·v₁² and the initial kinetic rotational energy, 1/2·m·ω₁² are 0
∴ K₁ = 0 + 0 = 0
The final potential energy of the student when lands. P.E.₂ = m·g·h₂ = 0
Where;
h₂ = 0 m
The final kinetic energy, K₂, of the wheel and student is give as follows;
Where;
v₂ = The speed of the student just before she lands
ω₂ = The angular velocity of the wheel just before she lands
By the conservation of energy, we have;
P.E.₁ + K₁ = P.E.₂ + K₂
∴ m·g·h₁ +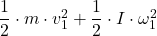 = m·g·h₂ +
= m·g·h₂ + 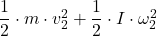
Where;
ω₂ = v₂/r
∴ 5061.96 J + 0 = 0 +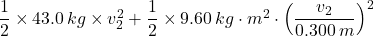
5,061.96 J = 21.5 kg × v₂² + 53.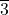 kg × v₂² = 21.5 kg × v₂² + 160/3 kg × v₂²
kg × v₂² = 21.5 kg × v₂² + 160/3 kg × v₂²
v₂² = 5,061.96 J/(21.5 kg + 160/3 kg) ≈ 67.643118 m²/s²
v₂ ≈ √(67.643118 m²/s²) ≈ 8.22454363 m/s
The speed of the student just before she lands, v₂ ≈ 8.225 m/s.