Share
Water at 20oC flows through a long elliptical duct 30 cm wide and 22 cm high. What average velocity, in m/s, would cause the weight flow to
Question
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Answers ( )
Explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Fluid is water so, density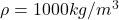
Weight flow rate = 500 lbf/s = 2224.11 N/sec
Cross-sectional area (A) =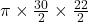
= 0.05184
Hence, weight flow rate will be given as follows.
w =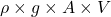
2224.11 N/sec =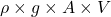
V =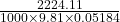 m/s
m/s
= 4.373 m/s
Thus, we can conclude that average velocity in the given case is 4.373 m/s.
Answer:
Explanation:
length of major axis, 2a = 30 cm
a = 15 cm = 0.15 m
length of minor axis, 2b = 22 cm
b = 11 cm = 0.11 m
Weight flow, mg = 500 lbf/s = 2224.1 N/s
Area of duct, A = π ab = 3.14 x 0.15 x 0.11 = 0.0518 m²
Let v be the velocity
Volume per second = mass per second / density
Area x velocity = mass per second / density
0.0518 x v = 2224.1 / (9.8 x 1000)
v = 4.4 m/s