Share
A spherical shell rolls without sliding along the floor. The ratio of its rotational kinetic energy (about an axis through its center of mas
Question
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Answers ( )
Answer:
The ratio is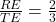
Explanation:
Generally the Moment of inertia of a spherical object (shell) is mathematically represented as
Where m is the mass of the spherical object
and r is the radius
Now the the rotational kinetic energy can be mathematically represented as
Where is the angular velocity which is mathematically represented as
is the angular velocity which is mathematically represented as
=>![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com w^2 = [\frac{v}{r}] ^2](https://documen.tv/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93d6e9a476081f09ee5719ee8cb1aa66_l3.png)
So
Generally the transnational kinetic energy of this motion is mathematically represented as
So