Share
In an aqueous chloride solution cobalt(II) exists in equilibrium with the complex ion CoCl42-. Co2 (aq) is pink and CoCl42-(aq) is blue. At
Question
In an aqueous chloride solution cobalt(II) exists in equilibrium with the complex ion CoCl42-. Co2 (aq) is pink and CoCl42-(aq) is blue. At Low Temperature the pink color pre-dominates. At High Temperature the blue color is strong. If we represent the equilibrium as:
CoCl4^2-(aq) <–> Co2+(aq) + 4Cl-(aq)
We can conclude that:___.
1. This reaction is:___.
A. Exothermic
B. Endothermic
C. Neutral
2. When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium constant, K:____.
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains the same.
3. When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium concentration of Co2:______.
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains the same.
in progress
0
Chemistry
4 years
2021-08-04T02:17:09+00:00
2021-08-04T02:17:09+00:00 1 Answers
221 views
0

Answers ( )
Answer:
1. This reaction is (A) Exothermic .
2. When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium constant, K: (A) Increases
3.When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium concentration of Co2: (A) Increases
Explanation:
1. The pink color predominates at low temperatures, indicating that the commodity is preferred.
This is a reaction that is exothermic.
2. As the decrease in the temperature , the equilibrium constant , K ;
equilibrium constant =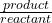 =
=![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{[CO^2^+][Cl^-^4]}{CoCl^2^-_4}](https://documen.tv/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ff4acd30bc6737c53543c3d65e31ffbf_l3.png)
As the temperature drops, the concentration of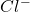 and
and 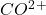 rises, and K rises as well , thus it increases .
rises, and K rises as well , thus it increases .
3. The equilibrium concentration of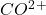 decreases as the temperature decreases:
decreases as the temperature decreases:
When the temperature is lowered, the equilibrium shifts to the right , that is it increases.